Do you ovulate on birth control?
Share
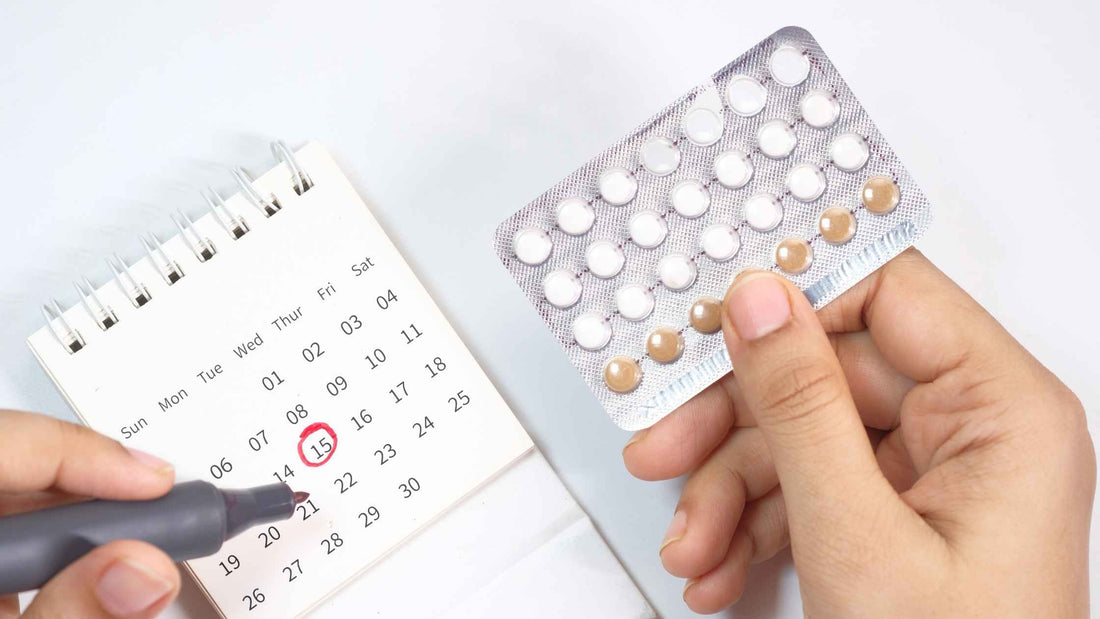
In short, no you do not ovulate when you're taking birth control. You may be surprised to learn that birth control pills can suppress ovulation in women. If you take oral contraceptives, or hormonal birth control pills, you generally do not ovulate.This is because the hormones in birth control can interfere with your natural hormone cycle.
How does birth control affect ovulation?
Ovulation is a process that occurs when ovarian cells release eggs. If ovulation occurs, the egg can be fertilized with the help of the sperm. No ovulation means there is no egg for sperm to fertilize, so you can't get pregnant. In women who don't take birth control pills to prevent pregnancy, ovulation is usually in mid-cycle. During a typical 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs approximately two weeks before the start of your next period. Sperm live from 3 to 5 days in female reproductive tissue and the egg can be fertilized by sperm for 12 to 24 hours after it's released. Also, the hormones in birth control pills thicken the mucus in your cervix making it much harder for sperm to swim to an egg.
How does the pill prevent pregnancy?
When your birth control pill is taken at the same time every day, they are most effective at regulating your menstrual cycle for preventing pregnancy.
Combination birth control pills
Combination birth control pills contain both estrogen and progestin to help prevent ovulation from happening. In combination birth control pills 9 out of 100 women will have an accidental pregnancy.
Progestin-only birth control
Progestin-only birth control pill helps to prevent pregnancy by thinning the lining of the uterus and thickening cervical mucus which ultimately suppresses ovulation.
This is also referred to as the mini-pill. It isn't as effective as combination pills because it doesn't prevent ovulation as well. Because 13 out of 100 women become pregnant who use it.
The pill also doesn't protect against sexually transmitted infections or diseases. So it is still important that you use barrier methods like condoms to reduce your chance of getting these infections. We talk about different non-hormonal birth control options here.
Are progestin-only pills better than regular birth control pills?
You're still putting more hormones into your body, so there are always side effects that. However, using a progestin-only pill helps to avoid those estrogen-specific side effects such as water retention and migraines.
Some doctors say that using a progestin-only pill helps with a faster return to fertility. And with that, these are less effective at preventing pregnancy than a combination birth control pill.
When you might ovulate on your birth control pill
If you do not take your birth control pill every day at the same time, there may be enough hormones in your body that ovulation may occur.
What happens to your period on the pill?
Your period is not a real period, but a withdrawal bleeding. It's basically an artificial period which is why it tends to be much lighter than a regular period.
Side effects of birth control pills
The most common side effect of birth control pills is nausea and vomiting which usually goes away after the first few months, however you have to get through the first few months to get your body adapted. Other side effects can include:
- Breast tenderness
- Weight gain or loss
- Irregular bleeding
- Mood swings
-headaches and migraines
-missed periods
-decreased libido
-eye changes
Birth control options where you ovulate
Fertility Awareness Methods (FAMs)
Also known as natural family planning and rhythm methods, this program helps you monitor your ovaries to find out if ovulation is occurring in your body. You can also monitor your cervical mucus or your cycle in calendars.
Barrier methods
Using barrier methods such a condoms are also 98% effective when used correctly AND they don't affect your hormones.
Find more birth control options.
DISCLAIMER: This content was written for informational purposes to educate women only. It is not medical advice.